AI Sustainability Lab at HNEE (KIN'L)
The AI Sustainability Lab (KIN'L) is dedicated to the application and utilisation of artificial intelligence methods at the university and beyond in cooperation with other research institutions, companies and civil society. The focus is on machine learning as a sub-area of artificial intelligence. Computers should learn to recognise (complex) patterns and correlations. Models are trained by experts, usually on large data sets. With the AI sustainability lab, we want to support people at the university and beyond in applying machine learning or artificial intelligence in general to their research questions. We do not want to leave this potential unutilised in order to develop and establish more sustainable solutions. In addition to research and transfer to industry and society, the computing and storage resources and expertise of KIN'L can also be used in teaching.
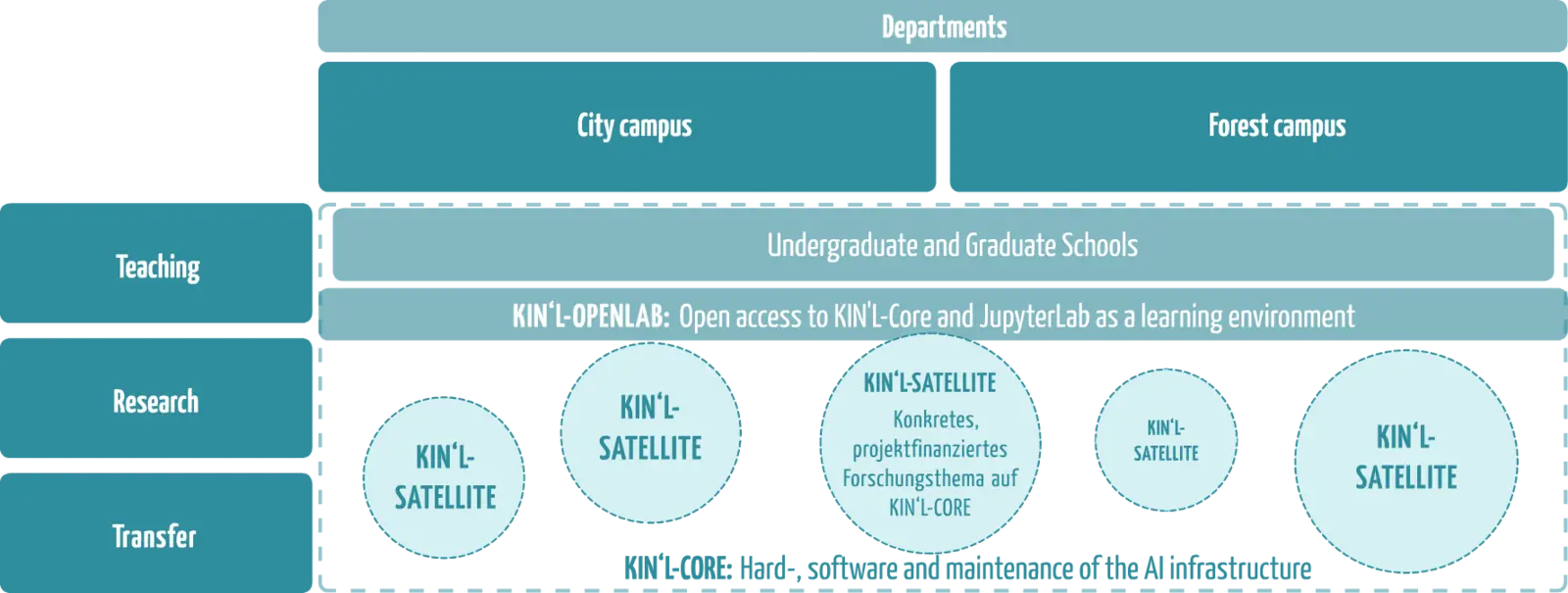
The KIN'L consists of
-
the KIN'L Core, which represents the basic computing and storage infrastructure,
-
the KIN'L OpenLab, as an open teaching and learning environment for the application of artificial intelligence methods on the KIN'L infrastructure, and
-
the KIN'L satellites, which work on specific, project-financed research topics.
The structural illustration of KIN'L on the right-hand side is intended to emphasise the university's public approach. The AI Sustainability Lab is open to anyone who wants to engage with technology in the context of research, teaching and transfer as well as its impact on people, society and nature - utilising opportunities and addressing risks.
With the AI Sustainability Lab, we can develop and operate models locally with the following advantages:
-
Contact persons and developers on site
-
Processing of personal data in compliance with data protection regulations
-
a low CO2eq footprint due to the use of renewable energies
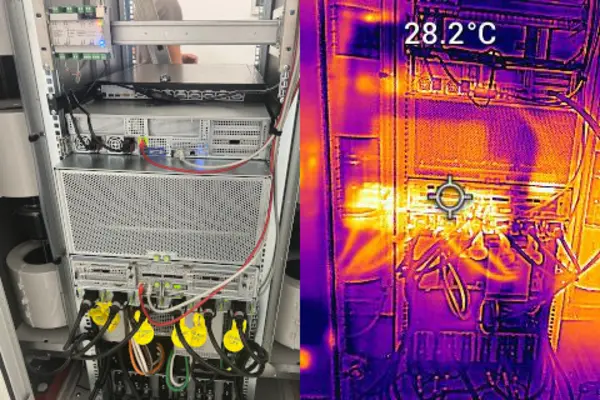
Our hardware and its thermal performance

Brandenburg AI Day 2024
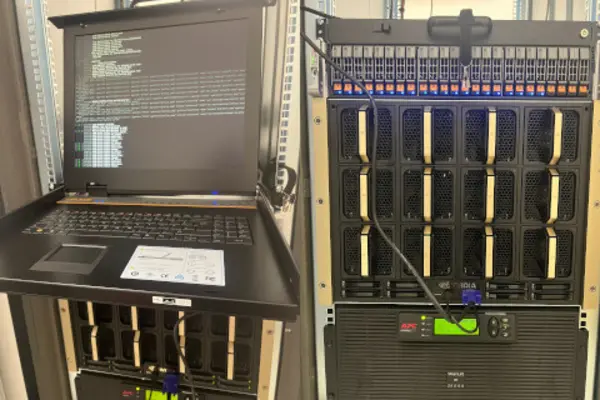

Our Hardware

We network for greater effectiveness.
KIN'L Core - the infrastructure of the laboratory
The computing and storage infrastructure (KIN'L-Core) consists of a computing system optimised for training deep learning models, but other models from the field of machine learning can also be calculated. The hardware used is an → Nvidia DGX H100 system with 8 H100 GPUs (640 GB GPU main memory in total) and 112 Intel® Xeon® cores and 2 TB main memory. The system offers 32 PetaFLOPS, i.e. 32 10^15 floating point operations per second, for 8-bit floating point numbers (FP8). If higher precision is required, the system offers less computing power at 16 PetaFLOPS for FP16 and BF16, 8 PetaFLOPS for FP32 and 480 TFLOPS for FP64 (see → NVIDIA Hopper Architecture). It is important to note that these figures represent peak performance and are therefore rather theoretical. In the actual implementation, these figures can serve as a guideline for optimising the program codes for efficient use of the hardware.
The computer system is connected to the storage system with 400 Gbit/s InfiniBand/Ethernet. Models and data can be stored there for fast access if the approximately 30 TB of NVMe storage space of the DGX system is not sufficient. The storage system has 18 NVMe SSDs, each with 30.72 TB, which results in approximately 550 TB, but not all of this is available, as the SSDs are configured redundantly in the file system (any two can fail) and SSDs also serve as hot spares to step in immediately in this case.
A server with a 32-core AMD EPYC CPU, 256 GB main memory and two Nvidia RTX A6000 GPUs is still available from previous procurements for smaller calculations.
Overall, these computing and storage systems form the basis for work with the AI sustainability lab.
KIN'L OpenLab - the KIN'L learning and experimentation environment
There are two main access options for using the infrastructure. On the one hand, access to the KIN'L core will soon be possible via JupyterLab. This is a web-based development environment that can be used via a browser. The integration of JupyterLab as part of → https://jupyter.hnee.de will take place over the next few months. Once this integration is complete, the KIN'L Core will be available for easy web-based use in KIN'L OpenLabs.
Access via Secure Shell (SSH) is already possible. SSH is a widespread and very common option for accessing remote systems in the Linux/Unix world. In this way, computers can be used via a command line. However, as this is not easy for many users, we will offer OpenLab via JupyterLab in the future.
In this way, the computing and storage resources of KIN'L can be used in teaching or with external partners from research, business and society.
KIN'L Satellites - AI-related research and transfer projects
The satellites in KIN'L enable the realisation of research and transfer projects using the KIN'L Core. Ideally, a project should approach us when applying for funding. This allows us to clarify whether and how the AI Sustainability Lab can help with the project. Even before applying for projects using artificial intelligence methods, KIN'L can use its AI expertise to help with the development and design of a project idea. With our experience in the application of artificial intelligence, we can sharpen ideas and categorise them in terms of feasibility.
Contact us
The AI Sustainability Lab organises events at irregular intervals. For example, we have already organised events to explore AI in research at the university. More will follow, as the topic of AI will not be leaving us any time soon.
Materials
As part of the AI Sustainability Lab, we have developed the following documents and learning resources:
-
Introductory presentation on KIN'L (July 2025)
-
Document on the onboarding of KINL users (in English)
-
Jupyter Notebook for the classification of sound (introductory example)
-
Jupyter Notebook for sentiment analysis of film ratings (advanced)
-
Jupyter Notebook for the classification of handwritten numbers (advanced)
The project has been funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) since 1 April 2023 as part of the AI-Nachwuchs@FH funding programme under the funding code 13FH009KI2 and will be further developed and operated as part of the → Center for Data Science after the funding period.

